Surety
What is Surety?
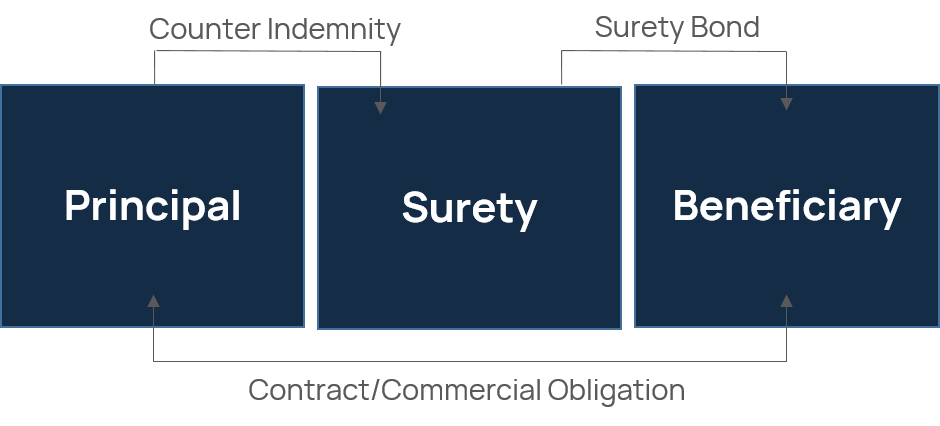
Surety is an obligation by a financial institution (which for our purposes is an insurance company) to guarantee the contractual or commercial obligations of one party, the Principal, to another, the Beneficiary.
Surety bonds can be required under the terms of a contract, or in accordance with statutory or licensing requirements, to secure the performance of the Principal in its commercial or contractual obligations to the Beneficiary.
As illustrated below, a surety bond is a tri-partite agreement issued by an insurer, the Surety, providing monetary compensation to the Beneficiary in the event that the Principal fails to perform its contractual or commercial obligations.
A counter-indemnity is taken from the Principal (and potentially its parent company) allowing the Surety to seek reimbursement in the event the Surety has to pay a claim under the surety bond.
Why choose Howden?
- Pricing: consistently delivering competitive terms.
- Market influence: as a leading income generator to the surety insurers we have excellent buying power.
- Bespoke solutions: surety solutions for challenging, innovative and complex transactions.
- Global & local solutions: facilities on a local, regional or global basis.
- Delivery capacity: access to all major providers ensures all capacity options are fully explored.
- Industry expertise: expertise across multiple industry sectors.
- Syndication: organisation of multiple surety capacity to meet large surety bond requirements.
- Document analysis: market leading surety bond review capabilities including the analysis of contract.
- Facility management: full service administration of all day to day surety bond needs and arrangement of competitive surety bond facilities.
Surety Bond Types
Surety is traditionally divided into two categories
| Contract | Commercial |
|---|---|
|
|
Surety bonds are widely used and are a critical financial tool in many industries:
|
|
Insurer vs Bank
Why are insurer issued surety bonds superior to bank surety?
Bonds issued by a bank diminish available headroom under lines of credit and can limit opportunities for growth.
Insurers generally issue surety bonds on an unsecured basis, being provided on the assessment of a company's financial strength and proven track record. The issuance of surety bonds by an insurer does not impact working capital or bank borrowing facilities and therefore can provide a useful boost to a company's liquidity.
